Bull's eye levels and screw-on levels
Definition of terms
A spirit level is hollow body filled with a fluid and a gas bubble which is used to check the horizontal position of an object.
The position of the gas bubble in the fluid shows the angle and the direction at which the object is inclined in relation to the horizontal level.
The function
The hollow body containing the fluid and the gas bubble has a defined radius at its topic side, causing the gas bubble to float by its buoyancy always to the highest point.
The transparent upper section normally carries markings or a circle centric to the biddle position. If the gas bubble is centered precisely inside the merking and if the air level is properly adjusted, the object to be checked is in the horizontal position.
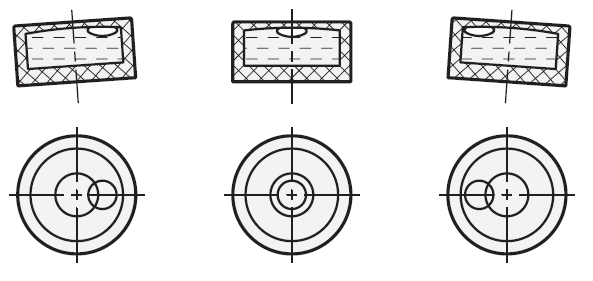
Types of spirit levels
Spirit levels are available as bull´s eye levels or screw-on levels.
Bull´s eye levels simultaneously measure the angle of inclination and the angular position, e.g. of a certain level, whereas screw-on levels indicate the angle of inclination in one dimension only along the axis of the level.
Sensitivity
The sensitivity of spirit levels is given as angle of inclination, e.g. 30 angular minutes or 0.5 degrees. This is the angle of inclination by which the spirit level must be tilted to make the bubble move by 2 mm. A spirit level with a sensitivity of 6 angular minutes therefore has a higher sensitivity than a spirit level with a sensitivity of 30 angular minutes.
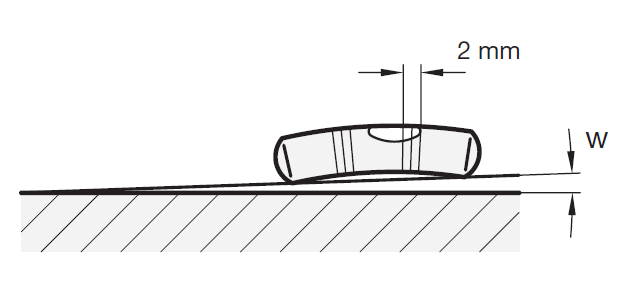
Angle of inclination and difference in altitude
Sensitivity is sometimes also given in millimetre per metre, i.e. as difference in altitude per unit of the length.
See also the reference table opposite.
| Difference in altitude | Angle w | |
|---|---|---|
| in milimetre per metre | in angular minutes | Degree, decimal |
| 0.3 | 1 | 0.0167 |
| 0.9 | 3 | 0.0500 |
| 1.7 | 6 | 0.1000 |
| 2.9 | 10 | 0.1667 |
| 5.8 | 20 | 0.3333 |
| 8.7 | 30 | 0.5000 |
| 11.6 | 40 | 0.6667 |
| 14.5 | 50 | 0.8333 |
| 17.5 | 60 | 1.0000 |
-
Generals
-
1. Plastic materials
- 1.1 Mechanical strength
- 1.2 Thermal resistance
- 1.3 Strength and surface hardness
- 1.4 Resistance to chemical agents
- 1.5 Resistance to atmospheric agents and uv rays
- 1.6 Flame resistance
- 1.7 Electrical properties
- 1.8 Surface finish and cleanability
- 1.9 Compliance with international standards
- 1.10 Competence of Elesa+Ganter technical department
- 2. Metal materials
- 3. Other materials
- 4. Machining tolerances
- 5. Fixed handles
- 6. Assembly measures
- 7. Special executions
- 8. Colours
- 9. Test values
-
10. Technical tables
- 10.1 Conversion tables
- 10.2 DIN 79 Square holes and shafts
- 10.3 DIN 6885 Keyways
- 10.4 GN 110 and GN 110.1 Transversal holes
- 10.5 DIN 13 ISO Metric threads
- 10.6 DIN 228 Cylindrical GAS-BSP threads
- 10.7 DIN EN ISO 898-1 | DIN EN 20898-2 Strenght values
- 10.8 DIN ISO 286 ISO-Fundamental tolerances
- 10.9 IP Protection Classification
- 10.10.1 PFB | PRB Thread locking with jamming action Polyamide patch coating/ Polyamide complete coating
- 10.10.2 MVK Thread locking gluing Micro encapsulation precote 80 (red)
- 10.11 Stainless Steel characteristics
- 10.12 Surface treatments
- 10.13 Carbon steel, zinc alloys, aluminium, brass characteristics
- 10.14.1 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.14.2 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.14.3 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.15 Load ratings U-Handles
- 10.16 Load ratings metal hinges
- 10.17 Strength of indexing plungers
- 10.18 Assembly sets GN 965 and GN 968
- 11. Vibration-damping elements
-
1. Plastic materials
- Hygienic design
- Operating Elements
- Clamping knobs
- Control elements
- Rotary controls
- Indexing elements
- Joints
- Transmission elements
- Levelling elements
- Hinges
- Latches
- Toggle, power and hook clamps
- Accessories for hydraulic systems
- Tube clamp connectors
- Castors and wheels
- Magnets
- Conveyor components
- Linear slides
- Vibration mounts
- Vacuum components
- Elastomer springs